Practical Demonstration of Session Fixation Authentication Bypass Vulnerability in WebGoat Web Application.
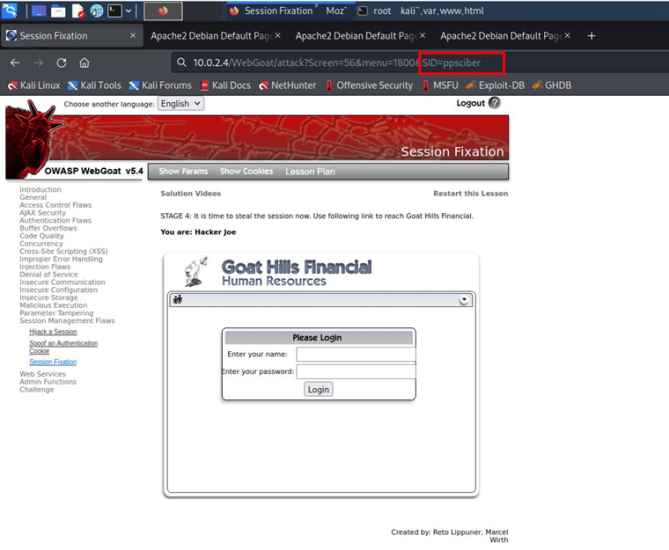
Once we have the following window open, we proceed to type a SID to steal the victim's session.
Click on "Send Mail".
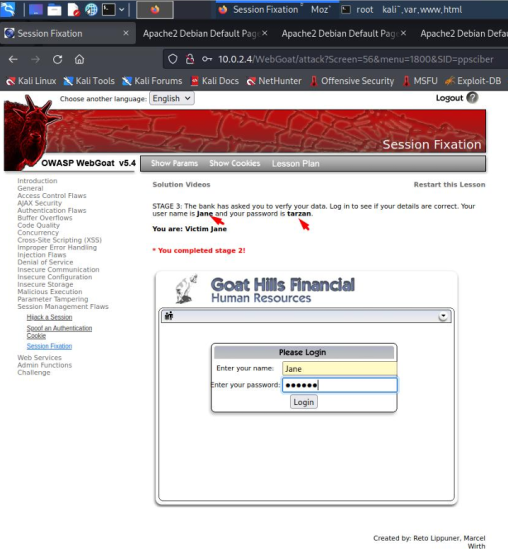
On this screen, the username and password are provided. We will enter them into the login and proceed to the next window.
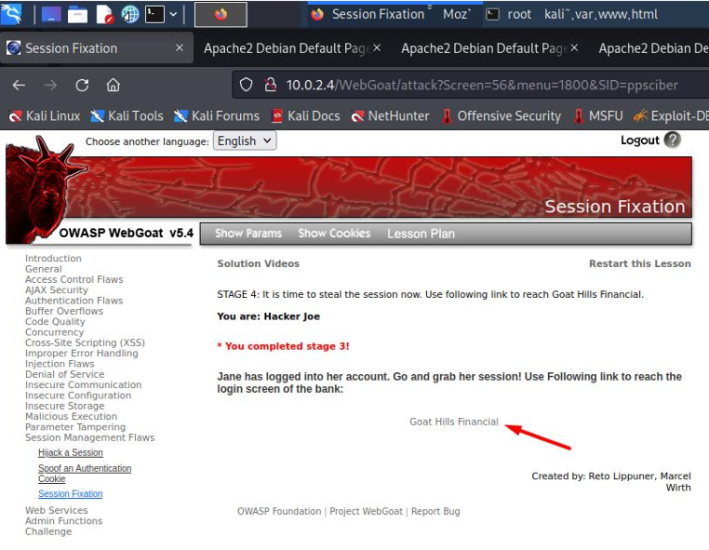
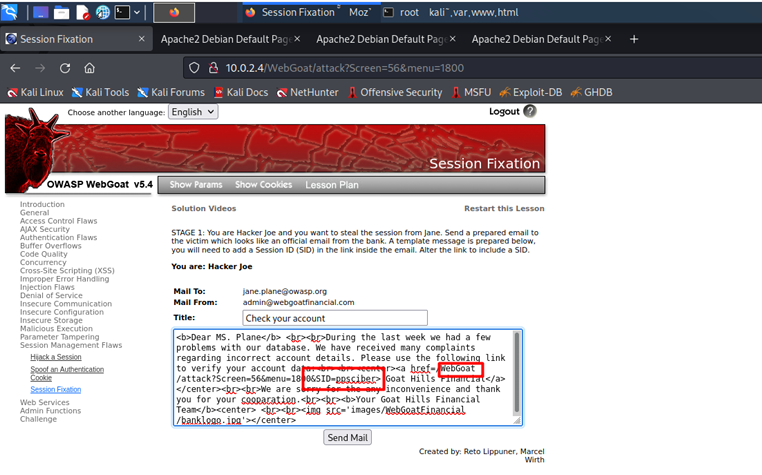
When the victim has logged in with their credentials, the attacker proceeds to fix the victim's session. To do this, we must click on the link.
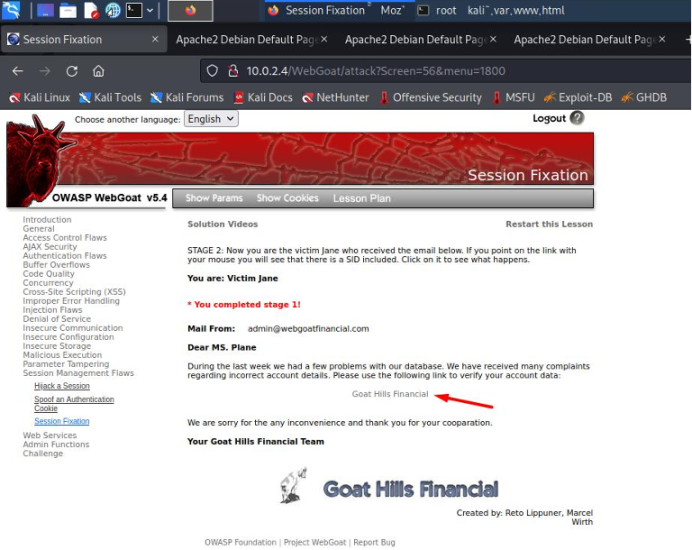
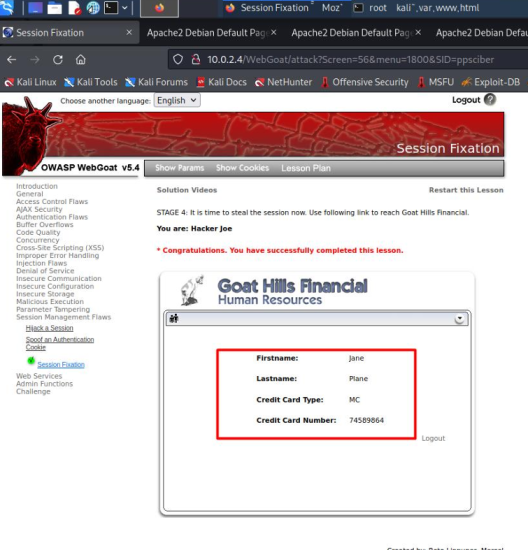
The link takes us to the victim's bank login. The attacker must type the SID that we added in the first screen into the URL to fix the session.
Once the session is fixed, we will have access to the victim's bank.
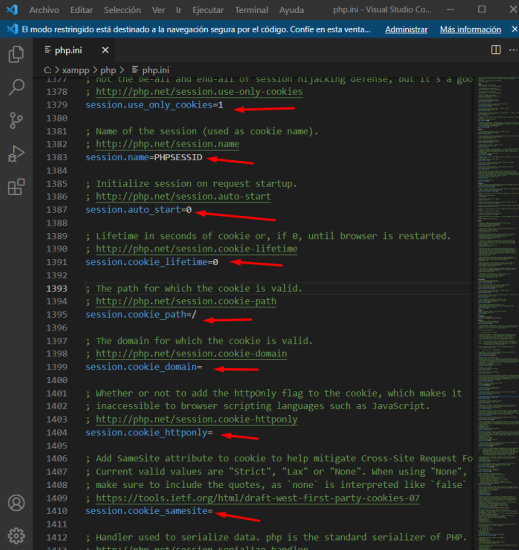
Locating PHP Session Management Configuration Parameters to Mitigate Potential Attack Success.
- Session.use_only_cookies Specifies whether the module will only use cookies to store the session ID on the client side. Enabling this setting prevents attacks involving passing the session ID in the URL. Default is 1 (enabled).
- Session.name Specifies the name of the session which is used as a cookie name. It should only contain alphanumeric characters. Default is PHPSESSID.
- Session.auto_start Specifies whether the session module automatically starts a session when a request starts. Default is 0 (disabled).
- Session.cookie_lifetime Specifies the lifetime of the cookie in seconds that is sent to the browser. A value of 0 means "until the browser closes". Default is 0.
- Session.cookie_path Specifies the path to be set in the session cookie. Default is /.
- Session.cookie_domain Specifies the domain to be set in the session cookie. Default is none, meaning the hostname of the server that generated the cookie according to the cookie specification.
- Session.cookie_httponly Marks the cookie as accessible only through the HTTP protocol. This means that the cookie will not be accessible by scripting languages, such as JavaScript. This setting can effectively help reduce identity theft through attacks (although it is not supported by all browsers).
- Session.cookie_samesite Allows servers to assert that a cookie ought not to be sent along with cross-site requests. This assertion enables user agents to mitigate the risk of information leakage, and provides some protection against cross-site request forgery attacks. An empty value means no SameSite cookie attribute will be set. Lax and Strict mean the cookie will not be sent cross-domain for POST requests; Lax will send the cookie for GET requests cross-domain, while Strict will not.
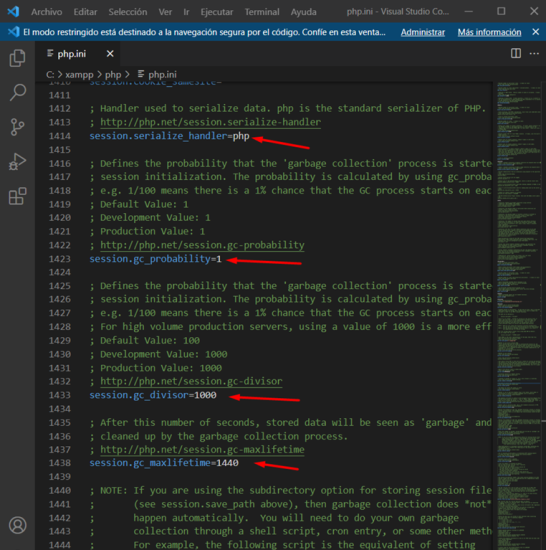
- Session.serialize_handler Defines the name of the handler used to serialize/deserialize data. PHP's serialization format (name php_serialize), PHP's internal formats (name php and php_binary). php_serialize internally uses a pure serialization/deserialization function and does not have the limitations that php and php_binary have. Older serialization handlers cannot store numeric or string indices containing special characters (and!) in `$_SESSION`. Use php_serialize to avoid errors with numeric indices or special characters at script shutdown. Default is php.
- Session.gc_probability Used in conjunction with session.gc_divisor to manage the probability that the garbage collection (gc) routine is started. Default is 1.
- Session.gc_divisor Defines the probability that the garbage collection (gc) process is started on each session initialization. The probability is calculated using gc_probability/gc_divisor, e.g., 1/100 means there is a 1% chance that the GC process will start on each request. Default is 100.
- Session.gc_maxlifetime Specifies the number of seconds after which information is seen as 'garbage' and potentially cleaned up. Garbage collection can happen during session startup (depending on session.gc_probability and session.gc_divisor).
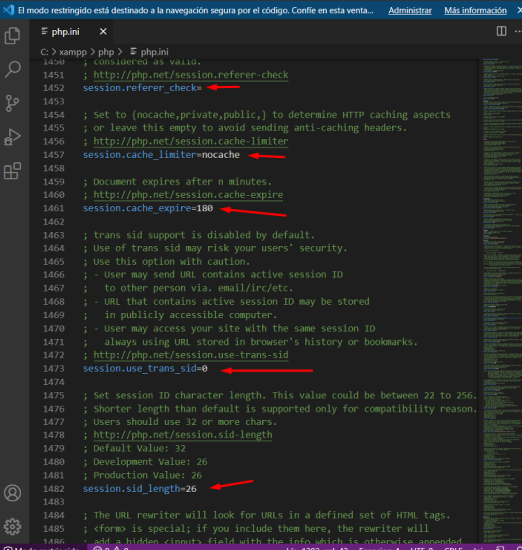
- Session.referer_check Contains the substring to check each HTTP Referer. If the Referer was sent by the client and the substring was not found, the embedded session ID will be marked as invalid. Default is an empty string.
- Session.cache_limiter Specifies the cache control method used by session pages. Can be one of the following values: nocache, private, private_no_expire, or public. Default is nocache.
- Session.cache_expire Specifies the lifetime in minutes for cached session pages, this has no effect for the nocache limiter. Default is 180.
- Session.use_trans_sid Whether transparent SID is enabled or not. Default is 0 (disabled).
- Session.sid_length Allows you to specify the length of the session ID string. This length can be between 22 and 256. The default value is 32. If compatibility is needed, 32, 40, etc., can be specified. Longer session IDs are harder to guess. At least 32 characters are recommended.
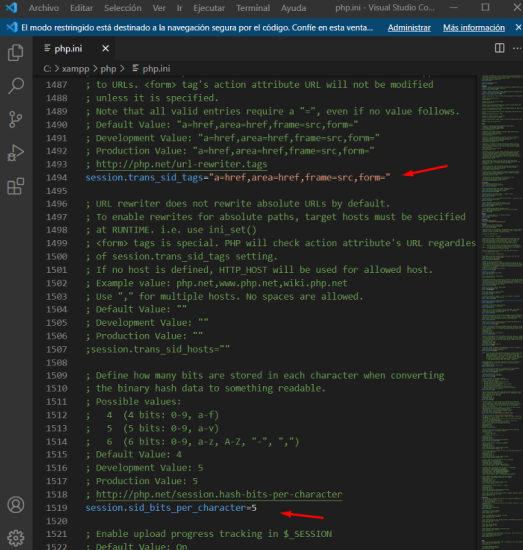
- Session.trans_sid_tags Specifies which HTML tags are rewritten to include the session ID when transparent SID support is enabled. Defaults are a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form= is a special tag. It is added as a form variable. `form`.
- Session.sid_bits_per_character Allows you to specify the number of bits in encoded session ID characters. Possible values are '4' (0-9, a-f), '5' (0-9, a-v), and '6' (0-9, a-z, A-Z, "-", ","). The default is 4. The more bits, the stronger the session ID. 5 is recommended for most environments.
Below are screenshots of the `php.ini` configuration:
References